Ethernet and SDH technologies are focused on computer and information networks. But the main problem in their interaction is pairing constant fixed speed SDH channels with pulsating Ethernet traffic. For example, VC-4 has a speed of 149.760 Mb / s, while Ethernet 100Base-T has a speed of 100 Mbit / s, respectively. Thus SDH payload channel is 70%, whereas the payload transmission GigabitEthernet generally drops to 40%. To solve these problems using technology GFP, VCAT and LCAS. In fact, these procedures have formed SDH network of the New Generation (NG SDH). Many network operators are given the opportunity to upgrade their networks instead of complete replacement of existing equipment.
Components NG SDH
It is believed that the SDH system belongs to a new generation, if it includes support for the following components:
- The general procedure for division into frames (General Framing Procedure, GFP), that provides the adaptation of asynchronous data traffic on the basis of variable length frames to byte-oriented SDH traffic with minimal latency and redundant headers; ITU-T G.7041.
- Virtual Concatenation (Virtual Concatenation, VCAT), allows the association at the logical level of a few containers VC-12, VC-3 or VC-4 in a data channel. ITU-T G.707, G.783.
- Driving adjust the channel capacity (Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme, LCAS) - allows you to implement any changes in capacity without interrupting data transmission. ITU-T G.7042.
GFP
GFP was created to replace these methods HDLC encapsulation data over SDH and simultaneously reduce the cost and complexity of implementation of the method in the equipment.
GFP encapsulation method supports services such as 10/100/1000 Mb / s Ethernet, IP, PPP, protocol SANs FiberChannel (FC), FICON, ESCON.
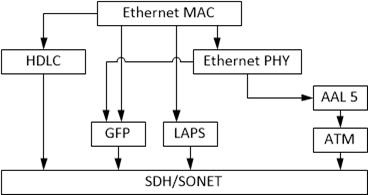
Map Ethernet traffic encapsulation GFP adapts the data stream based on variable-length frames to byte-oriented data stream SDH network, displaying various services in a general frame, which is then mapped into SDH frames. This frame structure better identifies and corrects errors and provides greater bandwidth efficiency than traditional methods of encapsulation.
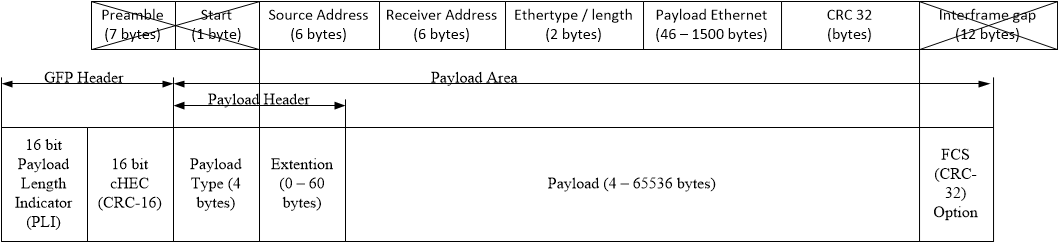
Formation of the GFP frame with Ethernet frames GFP frame contains the following components: main title (GFP Header), the title of the payload (Payload Header), the area of the payload (Payload Area), optional field error checking FCS payload.
The main header contains the length PLI frame GFP and cHEC field (core Header Error Control) to identify and header error correction.
cHEC used together with PLI to find the beginning of the frame (frame synchronization). This procedure uses the same principles as in the ATM technology to synchronize to the cell stream. First Receiver GFP frame is able to find the beginning of the frame (Hunt State), scanning the bit-by-bit and comparing the calculated CHEC for PLI with the received stream of CHEC. When a match is found, the unit goes into a state of Pre-Sync State in which it is already known to the starting point of the next frame GFP. If the next frame is calculated cHEC coincides with that obtained, it is assumed that frame synchronization is established and the receiver switches to normal sync Sync State.
Types client signal adaptation
The two types of client signal adaptation NG SDH networks are used: GFP-Framed (GFP-F) and GFP-Transparent (GFP-T).
GFP-F encapsulation method is focused on one single frame GFP client signal frame (PDU) and has the following features:
- PDU is buffered before encapsulation (because it has a variable length);
- PDU can be displayed for different transmission rates (including variable using VCAT / LCAS);
- Operates at Layer 2 (Layer 2), i.e. It uses byte sequence PDU, extracted from the physical layer;
- Title payload (Payload Header) provides information on the encapsulated protocol;
- Well suited for data traffic (Ethernet, IP), however delays may be unacceptable for protocol storage area network (SAN).
GFP-T method is focused on the signals using the coding 8B / 10B (Gigabit Ethernet, SAN protocols).
VCAT
In conventional SDH network is determined by the degree of detail of the transport band capacity containers VC-12, VC-3, VC-4 and related groups, for example, VC-4-4c - four contiguous VC-4.
Virtual Concatenation (association), certain recent ITU-T, eliminating restrictions related techniques. Virtual Concatenation logically connects the individual containers in a single compound. Any number of any type of containers (VC-12, VC-3 or VC-4) can be grouped together to form a logical channel
LCAS
The parameters that are responsible for the payment delay (512 ms) and ensure the integrity of all members of the group are transferred in the header of individual containers tract (H4 byte for VC-4 / VC-3 and K4 byte for VC-12). For this function is responsible LCAS protocol, which is one of the last developed standards for NG SDH. It is performed between two network elements (NE), connecting the user interfaces in the SDH network. Each byte H4 / K4 transmits a control package, consisting of information on virtual concatenation and LCAS protocol.
Functional diagram of Ethernet over SDH
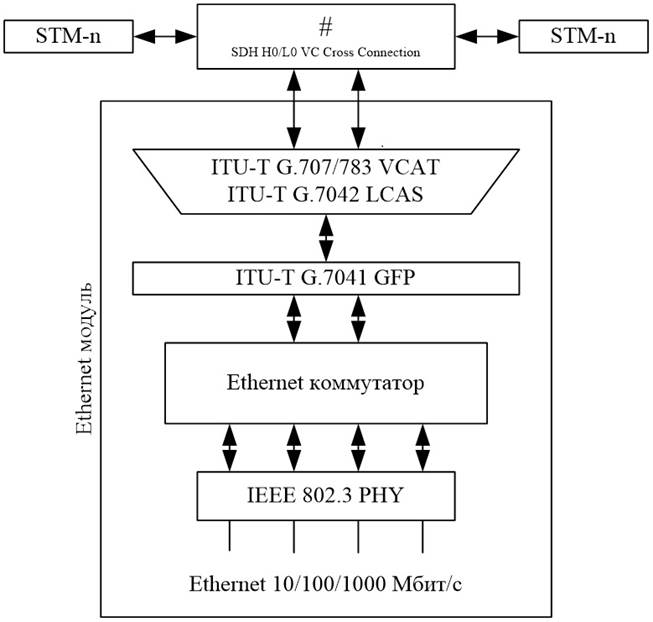
Functional diagram of Ethernet over SDH Built-in Ethernet switch is optional, but its presence is expanding set implemented in the Ethernet services. Built-in Ethernet switch support VLAN (802.1Q), technology Q-in-Q (802.1ad), prioritization 802.1p frames in combination with GFP, VCAT, LCAS and other features of SDH allow to build regional Ethernet network (Metro-Ethernet) Carrier Class .
