Campus Switching Architecture
Dell switches networking N-series are based on a modern architecture of campus networks
- Support loop redundancy without the use of STP by using MLAG protocol to create increased access to resources and high bandwidth.
- Smooth interoperability with existing infrastructure for greater compatibility and integration.
- Combining a variety of network products with the latest open standards protocol for more choice in network.
Campus architecture on Dell switches based on functional MLAG protocol launched in version 6.1 operating system, Dell Switches. In this architecture, the two switches N4064F as peers aggregate access switches, which are combined in two stacks as well as peers. Each stack switch maintains a portion of one floor in the building of the campus, which is aggregated with two 10Gbit / c uplink'ami. N4064F aggregation layer switches easily support up to 24 stacks of switches. This architecture provides improved bandwidth, overcoming limitations STP to block redundant ports. Network is designed with a high redundancy in terms of link failure and switches.
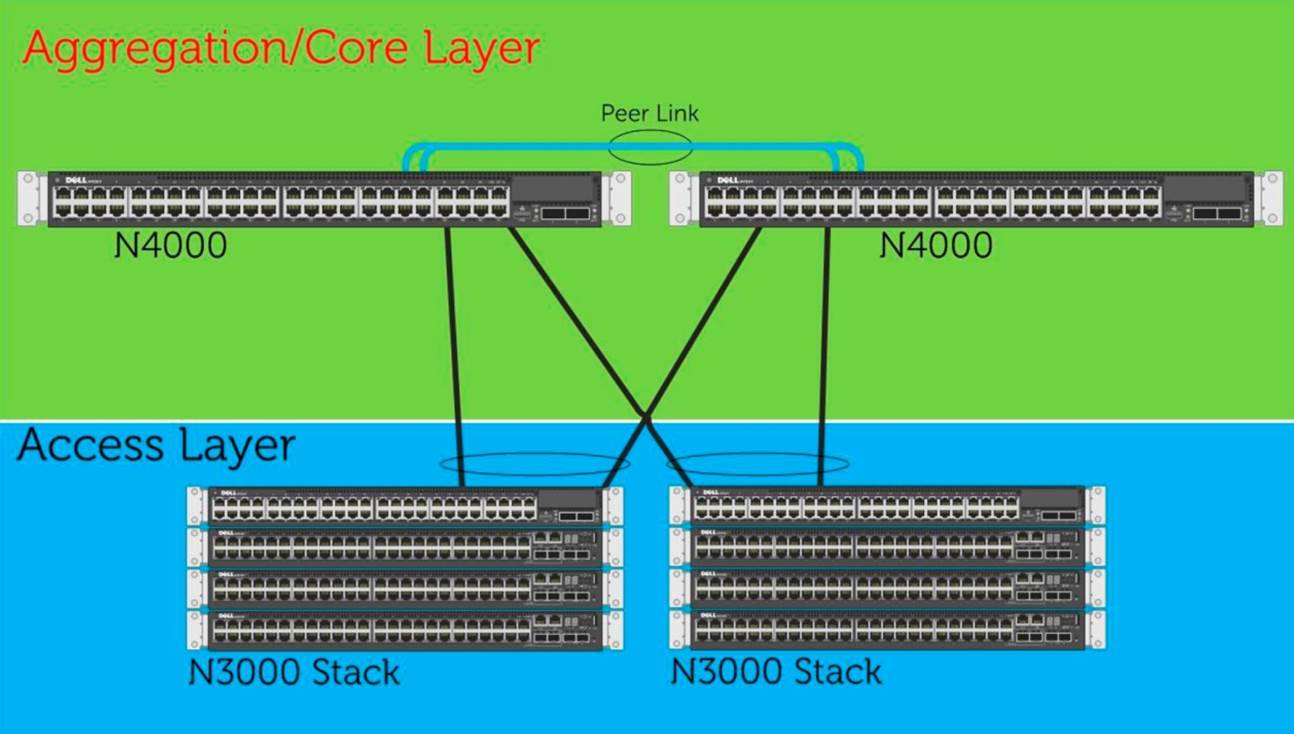
DELL Campus Switching Architecture
Multi-switch Link Aggregation (MLAG)
MLAG Technology (Multi-Switch Link Aggregation) enables two independent switches look like one logical switch to other devices without stacking.
Both switches can be administered separately, have different operating systems, adjust the operation. They should be interconnected Ethernet channels, in particular for the mirroring of the FDB table of MAC addresses. Requirements to devices connected to it by means of this technology is to support the standard LACP protocol.
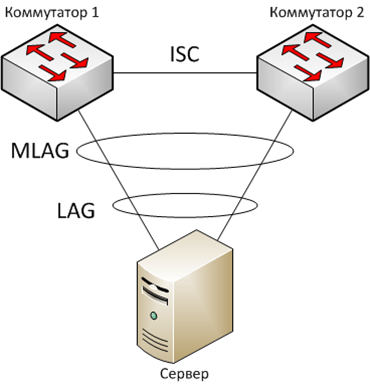
The need for MLAG arises when it is necessary to reserve the failure of the switch.
Interaction switches organizing MLAG carried out by Inter-Switch Connection, ISC. Action coordination is achieved through the exchange of messages between MLAG members of the group individually selected for this channel - Inter-Switch Connection, ISC. In order for the channel is not a loop, in normal operation, the traffic is blocked in it - this is one of the features of the work MLAG.
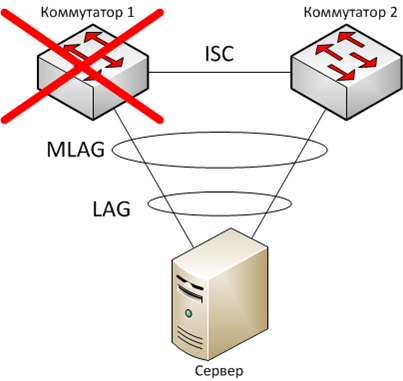
From a server perspective, their failure of one switch output will not result in degradation of service to a given topology.
All traffic will flow away smoothly on the link between the switch and the server 2.
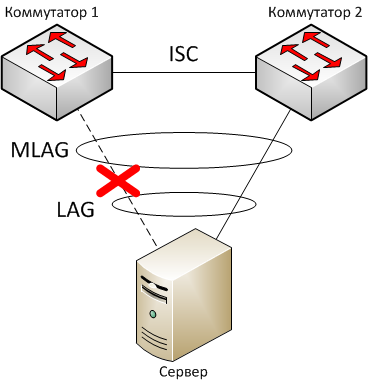
In the case of failure of the link between the server and any switch operation logic MLAG reduced to 'opening' the ISC and traffic redirect.
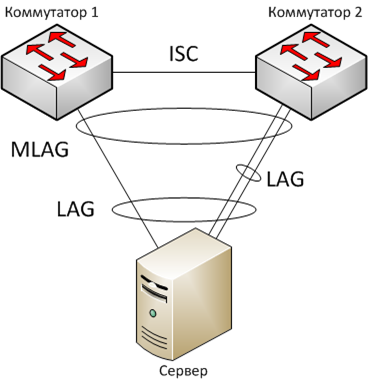
Using MLAG technology can be represented in another form. For example, you can include LAG MLAG
LACP - Link Aggregation Control Protocol
LACP - (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) sends packets that are called LACPDU, through all the interfaces of the device on which it is included. On the basis of these packages equipment determines the physical ports belonging to a particular logical channel. The protocol can operate in two modes:
- Passive mode, in which the equipment is waiting for the neighbor LACPDU packages and only then begins to send their.
- Active mode, in which the equipment constantly sends LACPDU packages.
To LACP earned, it requires the same rate and channel capacity. As a result of the work of establishing the LACP switches exchange the following information:
-
System Identifier (priority + MAC)
Port Identifier (priority + port number)
Operational Key (port parameters)
Balancing traffic in a LAG
Traffic balancing is performed by selecting a physical channel frame by the sender of the selected algorithm. The basic and commonly used include the following algorithms:
- MAC-based address of the sender or recipient of the MAC-address or given both addresses;
- on the IP-address of the sender or recipient's IP-address or given both addresses;
- on target port number or destination port number, or both ports are given.
Consider the example of two aggregated links using the balancing method of MAC-based address. In this case, the index will be used to balance the last bit of the MAC-address of the sender
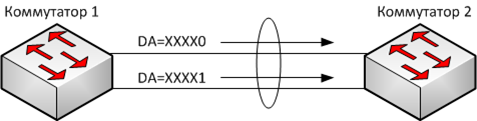
Balancing traffic in a LAG
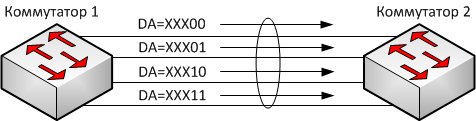
If records to be 4, then the last 2 bits of MAC-address to be used to balance
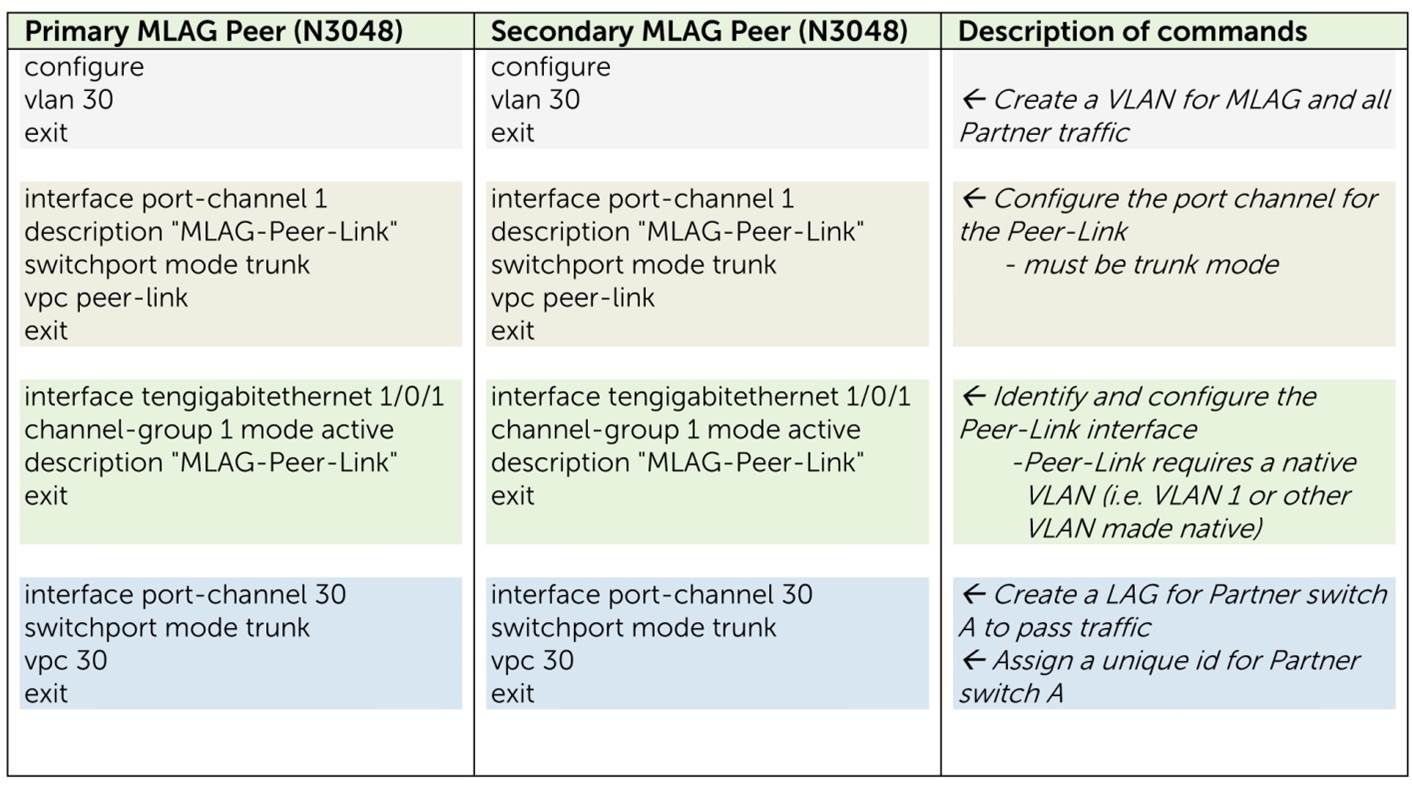
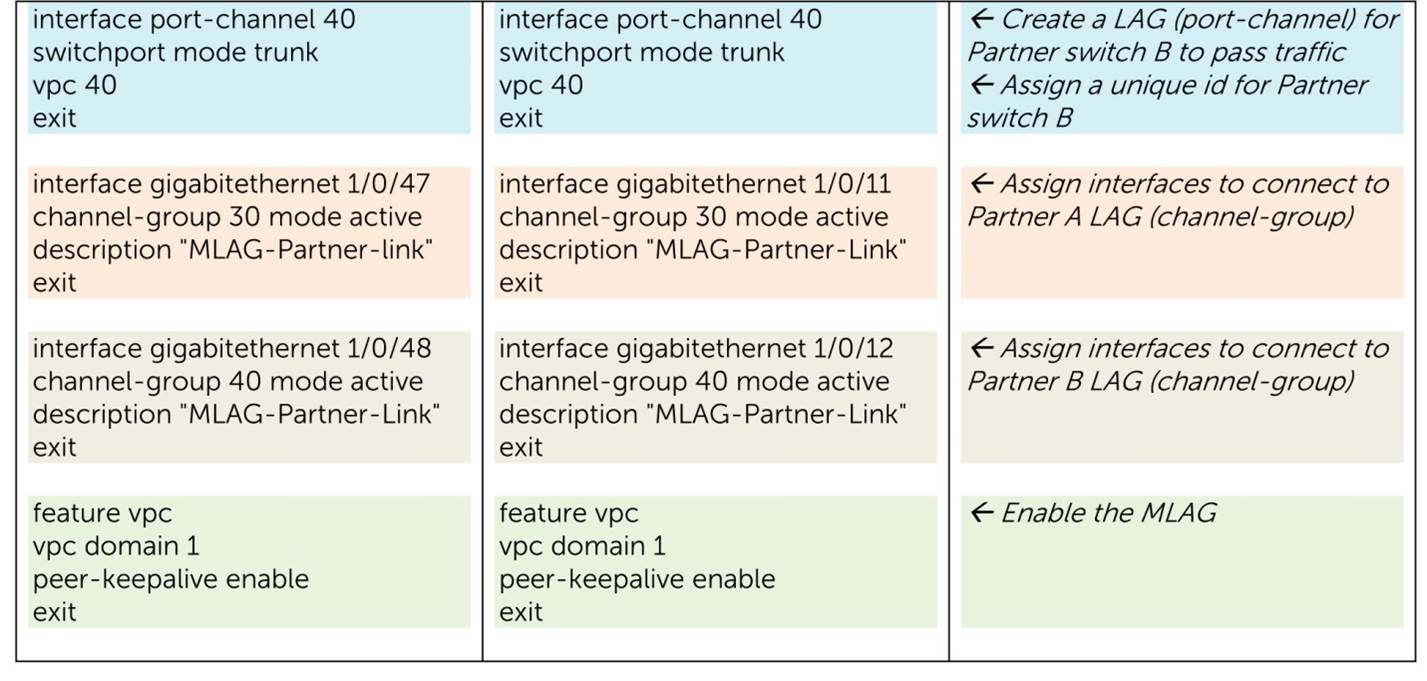
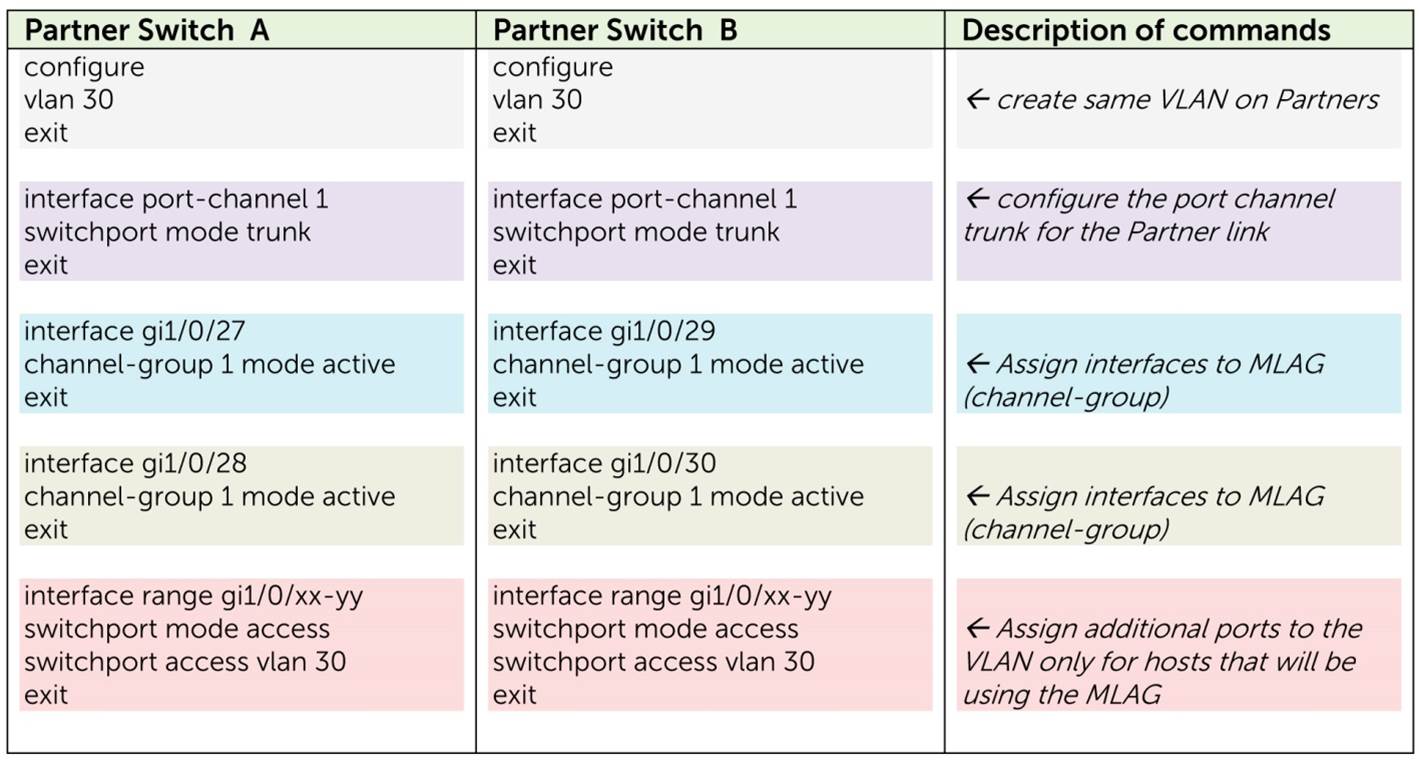
Configuration Example MLAG
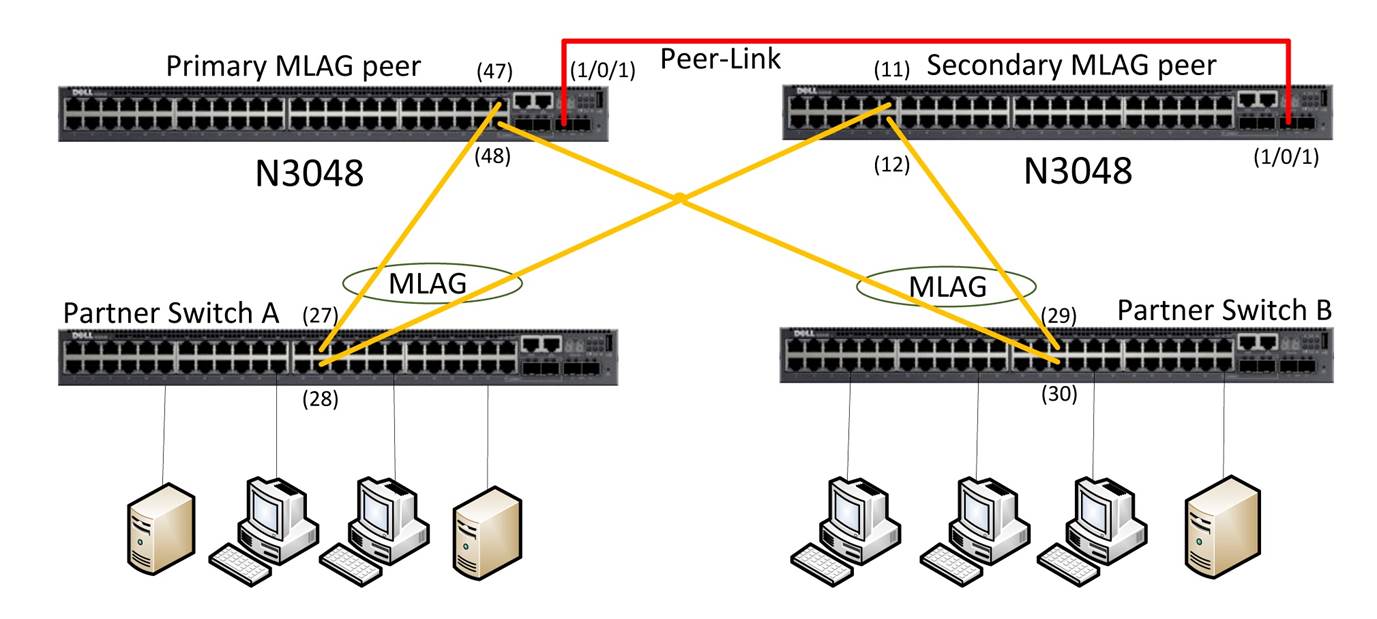
Configuration MLAG