Origin of Frame Relay technology is the end of the 80s. At this time, more and more began to receive the spread of reliable digital channels plesiochronous systems, synchronous digital hierarchy (PDH and SDH). These technologies provide a reliable high-speed channel with low noise and error.
X.25 protocol stack, which existed before the advent of Frame Relay, included a variety of systems error checking and recovery, as used in the low-speed channels with a large noise level. But with the advent of technologies PDH and SDH communication quality has improved significantly and eliminated the need for a complex system of checks, which was present in the X.25. As a result, the change of the protocol stack came Frame Relay technology, which had only the minimum necessary for delivering information from the sender to the recipient. It is also a breakthrough of this technology was that it provided a guaranteed bandwidth, which could provide early technology.
Transmission of frame in Frame Relay technology
Frame Relay technology uses a technique of virtual channels based on tags, thereby reducing the uncertainty in the data delivery to the recipient and this is not so tough methods of transmission, which is characteristic of primary and telephone networks.
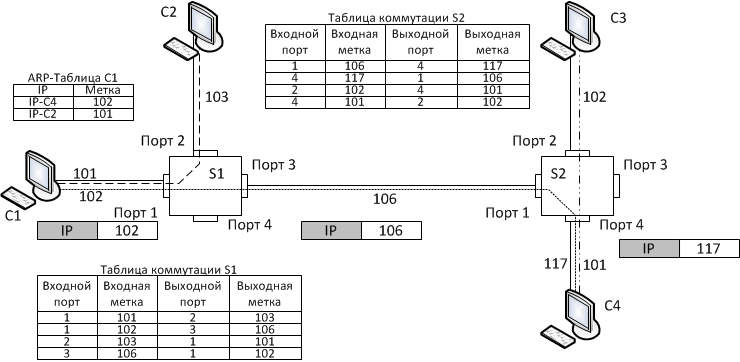
Transmission of frame in Frame Relay technology The virtual channel is established for the exchange of data between the nodes and made entries in the routing tables of all nodes through which this will take place. Set the input and output matching tags that mark the channel in the entire data path. Thus channels may be either unidirectional or bidirectional.
The mechanism of transmission channel package next. If the packet to be transmitted from the computer to the computers C1 C4, the packet is marked with the label 102 and is transmitted to the first node where the routing table of the package marks a new label 106 and is transmitted to the output port 3. Further to this mark, he gets to the second switch, and there gets a new tag 117, which gets on the computer C4.
Virtual Channel Label
Tag virtual channel is the local address of this channel, formally mark FR is the name of the DLCI (Data Link Connection Identifier - Data Link Layer connection identifier). Tags virtual channel should always be unique for each switch, and while they only make sense for the particular switches, ie they do not have values for the other switches and connections between switches must have agreed on the value of the mark.
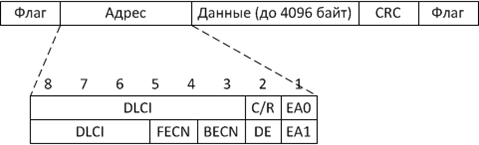
Метка виртуального канала Frame Relay
Bandwidth Guarantees
But the most interesting features of this technology to customers was a guarantee of bandwidth, which is divided into several types:
- Committed Information Rate, CIR - always guaranteed bandwidth below which transmission rate does not drop.
- Committed Burst Size, Bc - the maximum bandwidth that the provider can provide, but do not guarantee a similar data rate, since it does not fit the profile of CIR.
- Excess Burst Size, Be - the maximum number of bytes that the network will attempt to transmit in excess of the value of Sun for the time interval T.
