Under the topology of the network refers to the configuration of the graph, whose vertices correspond to the end nodes of the network (such as computers) and communications equipment (eg, routers), and the edges of the physical or informational communication between nodes.
Full mesh
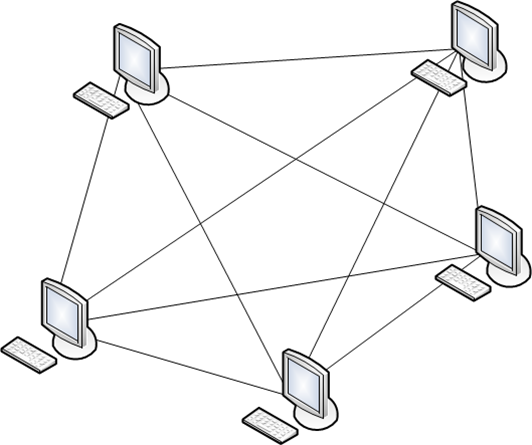
Full mesh This topology requires communication nodes N N (N-1) / 2 duplex physical links. The advantage of this layout is that it connects each node to each. Thus, in the event of a node failure, there is no malfunction of other nodes in the network based on this topology.
But in practice, this type of topology is not applicable, because it is a very expensive option of building a network.
The cellular topology
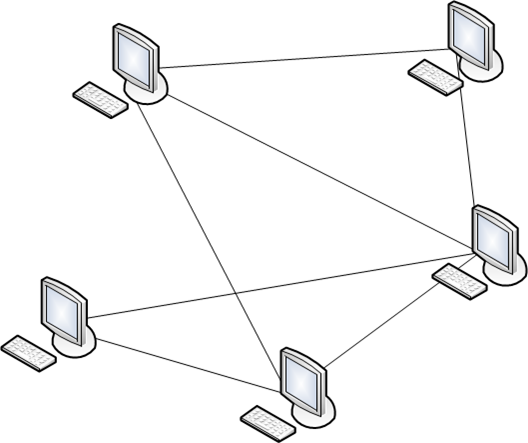
The cellular topology This topology is obtained from a full mesh by removing some of the links between nodes. In terms of reliability, this topology is less reliable than the fully connected, but at the same time and cheaper, by reducing redundant links to the organization costs.
This type of topology is often used in the Global (WAN) and metropolitan area networks (MAN). Technologies which employ these types of topologies may be systems like Ethernet and SDH / SONET systems.
Ring topology
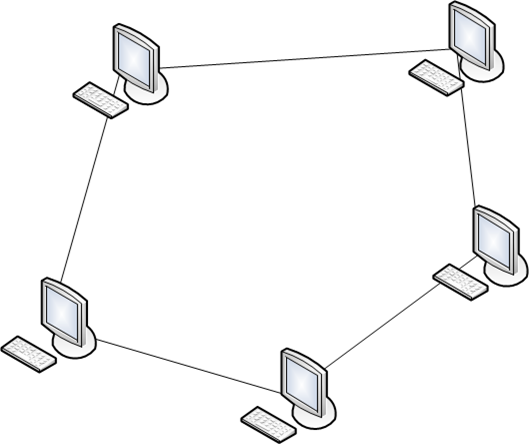
Ring topology In a ring topology, as the name implies, all components are combined into a ring. Data may be transmitted in the ring or in one of the directions, or both at once, depending on the network technology used in each particular case.
This topology is sufficiently reliable, because it provides samorezervirovanie. Each node is connected to two adjacent, and depending on the state of connections transmits data either clockwise or counterclockwise.
As a result, network redundancy is provided by the presence of two data paths from the start node to the end, as well as timely maintenance work on the data network in the event of failure of one node or one of the links.
The star topology
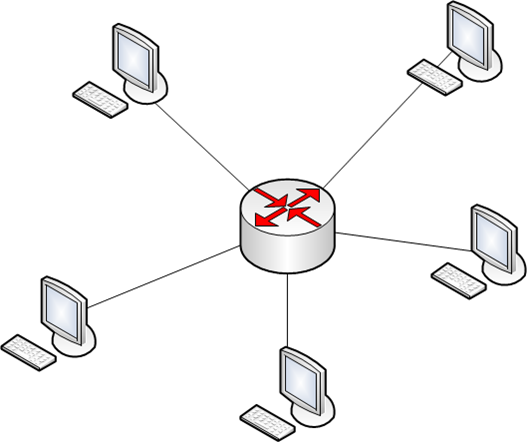
The star topology The appearance of a star topology is due to the advent of the telecommunication equipment, such as switches and hubs, which commute data transfer between end nodes on the network.
In this topology, the switch acts as a central hub through which the data transmission between other nodes.
The advantages of this topology are simplicity of data transmission networks, increase the efficiency of use of communication media, the ability to network administration and delimitation of user access to network resources.
The disadvantage is that the switch in this case is a critical point of failure, but in the case of the end-user (do not consider the role of the switch as the main unit, combining other switches) this circumstance is offset by the advantages of this topology.
Hierarchical star, tree
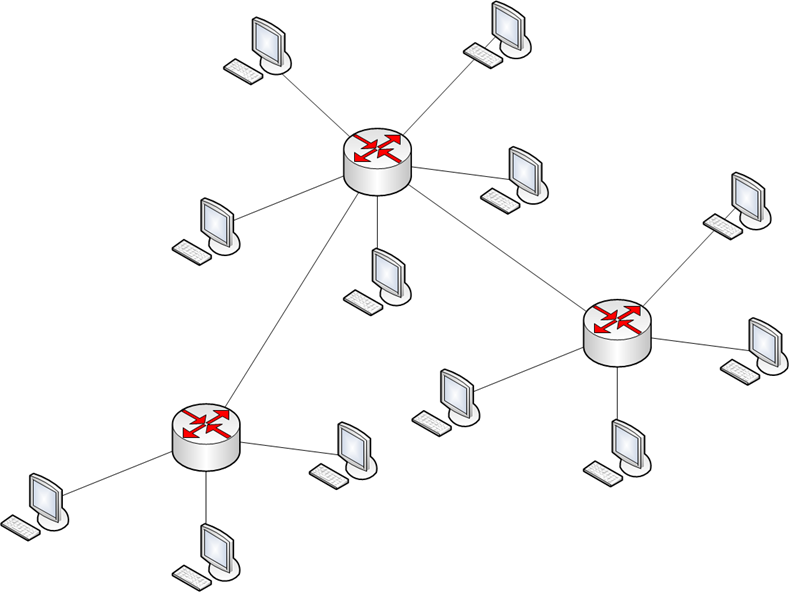
Hierarchical star, tree This topology is a common one for building modern data networks. In this case, the switches are combined into the main star, which organizes the main data channels, and depart from her branches, which connect the end-user nodes.
Redundancy in this topology affects only the main canals. This is achieved by an organization mesh topology between the switches or ring topology organization, again between switches.
