The optical fiber is a thin glass strand bilayer, each element (core and shell) has a different refractive index. The refractive index n of transparent material is the ratio of the velocity of light in vacuo (c - velocity of light) to the speed of light in this material (v), and defined by the following formula:
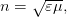
where ε and μ — respectively, relative dielectric and magnetic permeabilities.
Given that the relative magnetic permeability of the transparent material is usually constant and equal to one, the refractive index of the core for n 1 = √ε 1 , and for the shell n 2 = √ε 2 .
Refractive index of the shell is constant, and the core is generally a function of transverse coordinates. This function is called the refractive index profile.
For transmission of electromagnetic energy through an optical fiber is used the phenomenon of total internal reflection at the interface between two dielectric media, so it is necessary to n 1 > n 2 .
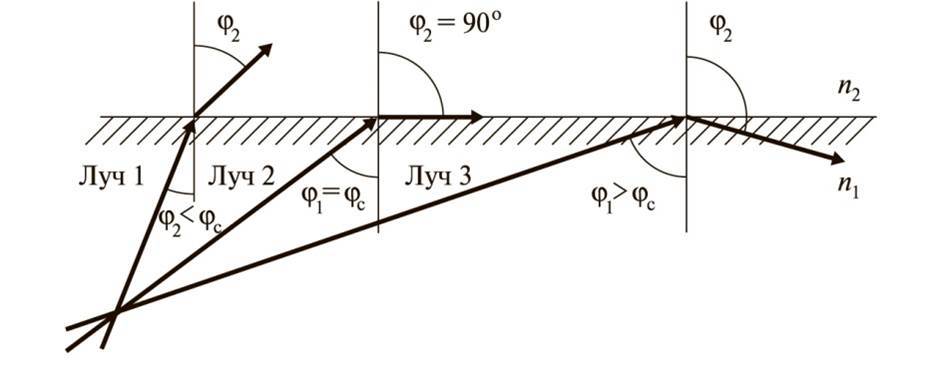
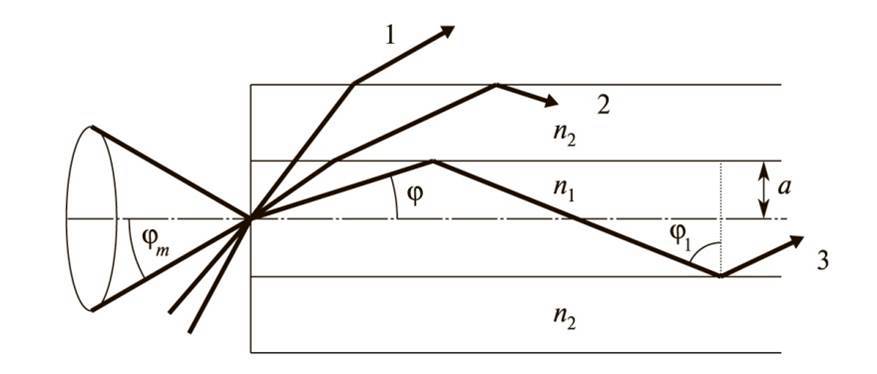

An important characteristic is the numerical aperture of the optical fiber NA , which represents the sine of the aperture angle φ .
Aperture angle — is the angle between the optical axis and forming a cone of light entering the end of the optical fiber, wherein φ 1 = φ c .
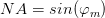
From NA values depend on the effectiveness of the input laser or LED in the optical fiber, microbending loss, pulse dispersion and the number of propagating modes.
