Table of contents
It is currently in beta (3.9.0b3), and in the future we will see a full release of Python 3.9. A few of the new features are just incredibly cool, and it will be awesome to see them in a full release.
We will cover the following points:
- Dictionary concatenation operator
- Typing
- Two new string methods
- New parser
Let's look at these innovations and how they can be applied.
Combining Dictionaries
One of my favorite features with good syntax. For example, if we have 2 dictionaries a and b that need to be combined, now we can use a special operator.
- a = {1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c'}
- b = {4: 'd', 5: 'e'}
- c = a | b
- print(c) # {1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 4: 'd', 5: 'e'}
As well as the update operator |= to update an existing dictionary:
- a = {1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c'}
- b = {4: 'd', 5: 'e'}
- a |= b
- print(a) # {1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 4: 'd', 5: 'e'}
If two different dictionaries have the same key, then use | :
- a = {1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 6: 'одинаковые ключи'}
- b = {4: 'd', 5: 'e', 6: 'но разные значения'}
- print(a | b) # {1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 6: 'но разные значения', 4: 'd', 5: 'e'}
Updating dictionaries with generators
Another interesting thing about the |= operator is the ability to update dictionaries with generators that have a key-value pair:
- a = {'a': 'one', 'b': 'two'}
- b = ((i, i**2) for i in range(3))
- a |= b
- print(a) # {'a': 'one', 'b': 'two', 0: 0, 1: 1, 2: 4}
When trying to perform such an action with the | we'll get a TypeError because the operator only allows union with dict objects
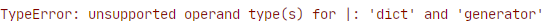
Typing
Python is a dynamically typed language, meaning we don't have to specify the type of a variable. This behavior is normal, although it can be confusing at times. And then suddenly Python's flexibility becomes nothing more than an inconvenience.
Since version 3.5, we can specify types for variables, but this approach was somewhat cumbersome. The update changes everything, take a look at the example:
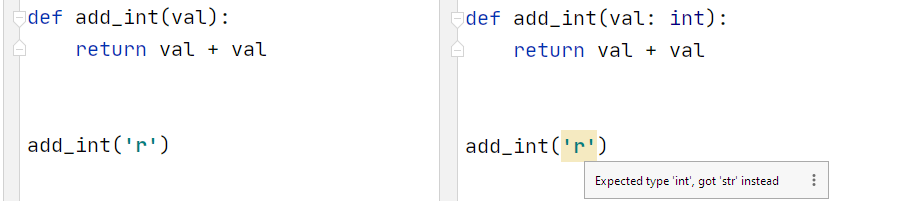 No typing (left) with 3.9 typing (right)
No typing (left) with 3.9 typing (right)
In the add_int function, we clearly want to add numbers to each other (for some cryptic and inexplicable reason). But our editor does not know this, and it is quite normal to add two lines using the + operator - therefore, we do not see any comments from the interpreter.
Now we can specify the int type we want to expect in the function's input. And now the interpreter will report the error immediately.
We can also specify nested types, for example:

Typing can be used everywhere - and all thanks to the new syntax, now it looks much more beautiful.

Two new string methods
Not as important as the other innovations mentioned above, but still useful in certain situations. Two new string methods to remove prefix and suffix:
- "Hello world".removeprefix("He") # "llo world"
- "Hello world".removesuffix("ld") # "Hello wor"
New parser
Although this change cannot be overlooked in any way, it may well become one of the most significant ones for the future development of Python.
Python currently primarily uses the LL(1) parser, which reads code from top to bottom and left to right.
Right now I don't really understand how this works - but I can give you a list of a few problems with this method:
Python contains not only the LL(1) parser, for this reason some parsers work bypassing the existing system, creating certain difficulties.
LL(1) creates a restriction on Python's syntax (with no way around them). This Issue highlights that the following code cannot be executed with
current parser (raised by SyntaxError):
- with (open("a_really_long_foo") as foo,
- open("a_really_long_bar") as bar):
- pass
- LL(1) breaks the left recursive parser. So a certain recursive syntax can provoke an infinite loop with a tree structure. Guido van Rossum, creator of Python, explains it here
All of these factors (as well as others I simply can't describe) have a forward-thinking impact on Python; they stop the development of the language.
A new parser based on PEG technology will give developers more flexibility to write code - something we'll start noticing from version 3.10 onwards.
Conclusion
That's all we can expect from the new version 3.9. If you can't wait to try out the new beta release - 3.9.0b3 - you can install it here
