After the game arena and targets were made and added, it is time to implement the targets hit, misses and charging system and cheating points.
Scoring system will be as follows:
- In the case of near misses, I propose to make the traces of bullet holes, a few species, and cheating on one point with a game account.
- In the case of the disappearance of the target on it without falling also make cheating a point from the game account.
- In the case of hitting the target charge between one and five points depending on how close to the hit had given.
The score will be displayed at the top of the playing field.
Project structure
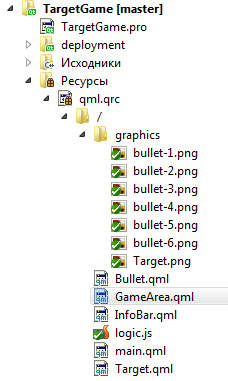
To achieve this you will need ideas, except the modification of the file, add the following files:
- InfoBar.qml - that will display information about the account;
- Bullet.qml - file describing the type of bullet holes;
- bullet-1.png, bullet-2.png, bullet-3.png, bullet-4.png, bullet-5.png, bullet-6.png - files with images of bullet holes;
Possible bullet holes are placed in the graphics folder to the same target image has been transferred.
Images of bullet holes
For a variety of several types of bullet holes similar to this will be applied.

GameArea.qml
Before proceeding to the consideration of the contents of the new file, refer to the changed content GameArea.qml file, as well as logical cores on javascript in logic.js file.
The main innovation here is the emergence of property scores for scoring, and the emergence InfoBar handler mouse clicks within the gaming arena.
Scores property contains the current scores and its value is passed to the property scores in infoBar to visualize the current account of the player.
When clicking on the gaming arena, which is equivalent to slip, bullet hole created object and per unit decreases the current account. A bullet hole is created in the same way as the creation of targets realized in the last lesson, ie using Logic logic core, which is in logic.js file.
- import QtQuick 2.7
- import "logic.js" as Logic
- Rectangle {
- id: grid
- ...
- property int scores: 0
- ...
- InfoBar {
- id: infoBar
- scores: grid.scores
- }
- // Create a trail of bullets when you click on the game arena
- MouseArea {
- anchors.fill: parent
- onClicked: {
- Logic.createBullet(grid, mouse.x, mouse.y)
- grid.scores--;
- }
- }
- ...
- }
logic.js
The core logic of the game will add only the creation of bullet holes. Processing logic hit the targets will be added in the file that describes the target.
- ...
- // Create a template for the bullet
- var bulletComponent = Qt.createComponent("Bullet.qml");
- ...
- // Create a trail of bullets
- function createBullet(parent, x, y)
- {
- bulletComponent.createObject(parent, {"x": x, "y": y});
- }
- ...
InfoBar.qml
InfoBar is a conventional RowLayout , which is nailed to the upper edge of the playing area, and stretched by its width. Current account will be displayed in a text field with id: scores . To set up external access to the text property of the text field, you must use the property alias.
- import QtQuick 2.7
- import QtQuick.Layouts 1.1
- RowLayout {
- height: 40
- anchors.left: parent.left
- anchors.right: parent.right
- anchors.top: parent.top
- anchors.leftMargin: 6
- anchors.rightMargin: 6
- spacing: 6
- z: 100
- // This property sets the access to the text field,
- // in which the current scores will be established
- property alias scores: scores.text
- Text {
- text: qsTr("Scores")
- font.pixelSize: 20
- verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter
- horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter
- }
- Text {
- // A text field with the current score
- id: scores
- font.pixelSize: 20
- verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter
- horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter
- }
- // Spacer, which RowLayout will move the text field to the left edge of the InfoBar
- Item {
- Layout.fillHeight: true
- Layout.fillWidth: true
- }
- }
Bullet.qml
Behavior bullet hole similar to the behavior of the target. The lifetime of the bullet hole is limited, and after the disappearance of the object is destroyed. The difference is, that is the offset coordinates (0, 0) in the middle of the object to the center of the object coincides exactly with the center point, which was committed cliques. A difference is also that in an array of object image from which to create a random selection is performed appearance bullet hole.
- import QtQuick 2.7
- import QtQuick.Window 2.2
- import "logic.js" as Logic
- Image {
- id: root
- width: 40
- height: 40
- // Set position coordinates (0, 0) in the center of the image
- transform: Translate {
- x: -width / 2
- y: -height / 2
- }
- // Set a list of possible array of bullets shot images
- property variant bullets: ["graphics/bullet-1.png", "graphics/bullet-2.png", "graphics/bullet-3.png",
- "graphics/bullet-4.png", "graphics/bullet-5.png", "graphics/bullet-6.png"]
- // When you create an object, select a random image
- source: bullets[Logic.getRandomRound(0, 5)]
- // The timer that will count down a random value from 3500 to 10000 ms
- // and after the disappearance of the run trace of bullets
- Timer {
- interval: Logic.getRandomRound(3500, 10000); running: true; repeat: false
- onTriggered: root.opacity = 0.0
- }
- // When the image is clear. we will destroy the object itself
- onOpacityChanged: {
- if (opacity == 0.0) {
- root.destroy()
- }
- }
- // Set the behavior of the animation properties of the object transparency
- Behavior on opacity { PropertyAnimation { duration: 100 } }
- }
Target.qml
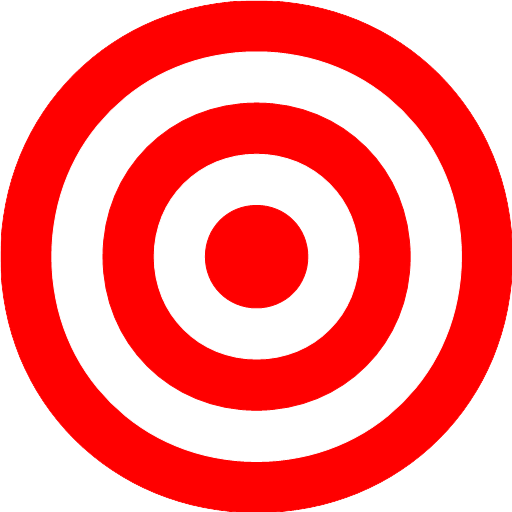

As you can see, there are five fields in which we assign a different value from 1 to 5 points.
In order to correctly calculate the hit on these areas, we need to apply the Pythagorean theorem. Remember? Of course the school trigonometry. The square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of cathetuses.
[latex]a 2 + b 2 = c^2[/latex]
So, this is the hypotenuse will range deflection hit the target from the center, well, the fact of getting on a given area will determine the radius of the circle, starting from the smaller circle. These checks are carried out in isHit() function declared in this file.
Also nuance here is that the target image is placed in the square, so that the region and also click the square, so if the click falls outside the scope of the great circle of the target, then we return 0 and pass click on in the gaming arena. To do this, you need to install propagateComposedEvents to true and prohibit accept mouse events, then it will be held in the lower lying objects to the coordinate z.
Also, do not forget to reduce the per unit expense of the game, if the target disappeared by itself without affecting the player. This is accomplished through a shared object from the logical core game, which stores the state of the gaming arena. That is, through Logic.gameState.scores.
- import QtQuick 2.7
- import "logic.js" as Logic
- Image {
- id: root
- ...
- // When the image is clear. we will destroy the object itself
- onOpacityChanged: {
- if (opacity == 0.0) {
- Logic.gameState.scores--
- Logic.destroyTarget(row, col)
- root.destroy()
- }
- }
- MouseArea {
- id: mouseArea
- anchors.fill: parent
- // This property determines whether the click event transmitted in lower lying elements,
- // ie those on the z-coordinate is below target
- propagateComposedEvents: true
- onClicked: {
- var scores = isHit(root.width/2, root.height/2, mouse.x, mouse.y);
- if (scores != 0) {
- // If the score is not zero, then we fix hit
- // Increase score and destroy the target
- Logic.gameState.scores += scores;
- Logic.destroyTarget(row, col);
- root.destroy();
- } else {
- // Otherwise, pass the click event in the lower lying elements along z
- mouse.accepted = false;
- }
- }
- }
- ...
- // Checking on the target hit.
- // Check the length of the line from the center to the point at the target hit
- // Depending on the length of the line relative to the radius of circles 5, which consists of the target
- // We determine how many points we get for hitting
- // a, b - the coordinates of the target center
- // x, y - coordinates of the point of hit
- function isHit(a, b, x, y)
- {
- var length = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(Math.abs(a - x), 2) + Math.pow(Math.abs(b - y), 2));
- if (length <= 5.6) {
- return 5;
- } else if (length <= 11.2) {
- return 4;
- } else if (length <= 16.8) {
- return 3;
- } else if (length <= 22.4) {
- return 2;
- } else if (length <= 28) {
- return 1;
- } else {
- // In this case, we were in MouseArea zone
- // which is a rectangle, but missed
- // at the target, which is a disk
- return 0;
- }
- }
- }
Conclusion
Now we have the expense and appearance of the application is as follows.
Download the source of Game sample on QML from GitHub

