Class QVector relates to a container class, and provides access to the items on the index, as well as a number of additional methods for ease of operation.
QVector instance of the class is essentially a one-dimensional array of objects. If you want to set as a vector of two-dimensional array, you can create an instance of a QVector , which will contain other instances QVector .
One-Dimensional array using QVector
For starters keep in Vector-dimensional array of type int:
QVector <int> myVector;
int massive[4] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
myVector.push_back(massive[i]);
qDebug() << "Value " << i << ": " << myVector.value(i);
}
And look at the output qDebug() :
Value 0 : 1 Value 1 : 2 Value 2 : 3 Value 3 : 4
The two-dimensional array in QVector
Now put in a two-dimensional vector array of int:
QVector <QVector <int> > myVector;
int massive[4][4] = { {1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12}, {13, 14, 15, 16} };
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
QVector<int> tempVector;
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
tempVector.push_back(massive[i][j]);
qDebug() << "Value " << j << ": " << tempVector.value(j);
}
myVector.push_back(tempVector);
qDebug() << "myVector " << i << ": " << myVector.value(i);
}
And look at the output qDebug() :
Value 0 : 1 Value 1 : 2 Value 2 : 3 Value 3 : 4 myVector 0 : QVector(1, 2, 3, 4) Value 0 : 5 Value 1 : 6 Value 2 : 7 Value 3 : 8 myVector 1 : QVector(5, 6, 7, 8) Value 0 : 9 Value 1 : 10 Value 2 : 11 Value 3 : 12 myVector 2 : QVector(9, 10, 11, 12) Value 0 : 13 Value 1 : 14 Value 2 : 15 Value 3 : 16 myVector 3 : QVector(13, 14, 15, 16)
An array of two-dimensional arrays using QVector
And if you want to keep all of two-dimensional arrays again in the vector, it can be done as follows:
QVector <QVector <QVector <int> > > myVector;
int massive[4][4] = { {1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12}, {13, 14, 15, 16} };
QVector <QVector <int> > matrix;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
QVector<int> tempVector;
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
tempVector.push_back(massive[i][j]);
qDebug() << "Value " << j << ": " << tempVector.value(j);
}
matrix.push_back(tempVector);
qDebug() << "matrix row " << i << ": " << matrix.value(i);
}
myVector.push_back(matrix);
qDebug() << "myVector: " << myVector.value(0);
And look at the output qDebug() :
Value 0 : 1 Value 1 : 2 Value 2 : 3 Value 3 : 4 matrix row 0 : QVector(1, 2, 3, 4) Value 0 : 5 Value 1 : 6 Value 2 : 7 Value 3 : 8 matrix row 1 : QVector(5, 6, 7, 8) Value 0 : 9 Value 1 : 10 Value 2 : 11 Value 3 : 12 matrix row 2 : QVector(9, 10, 11, 12) Value 0 : 13 Value 1 : 14 Value 2 : 15 Value 3 : 16 matrix row 3 : QVector(13, 14, 15, 16) myVector: QVector(QVector(1, 2, 3, 4), QVector(5, 6, 7, 8), QVector(9, 10, 11, 12), QVector(13, 14, 15, 16))
Conclusion
And finally, another way to work with vectors and arrays on the example of two matrices. which is somewhat different from the above the given methods. In this case, a matrix or two-dimensional array will contain one
QVector
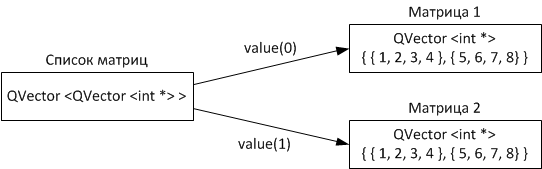
QVector <QVector <int *> > matrixList;
QVector <int *> matrix1;
QVector <int *> matrix2;
int massive1[2][4] = { {1,2,3,4}, {5,6,7,8} };
int massive2[2][4] = { {9,10,11,12}, {13,14,15,16} };
qDebug() << "Matrix 1";
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
matrix1.push_back(massive1[i]);
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
qDebug() << "[" << i << "]" << "[" << j << "]" << matrix1.value(i)[j];
}
}
qDebug() << "Matrix 2";
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
matrix2.push_back(massive2[i]);
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
qDebug() << "[" << i << "]" << "[" << j << "]" << matrix2.value(i)[j];
}
}
matrixList.push_back(matrix1);
matrixList.push_back(matrix2);
qDebug() << "Matrix 1 from matrixList";
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
qDebug() << "[" << i << "]" << "[" << j << "]" << matrixList.value(0).value(i)[j];
}
}
qDebug() << "Matrix 2 from matrixList";
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
qDebug() << "[" << i << "]" << "[" << j << "]" << matrixList.value(1).value(i)[j];
}
}
And look at the output qDebug() :
Matrix 1 [ 0 ] [ 0 ] 1 [ 0 ] [ 1 ] 2 [ 0 ] [ 2 ] 3 [ 0 ] [ 3 ] 4 [ 1 ] [ 0 ] 5 [ 1 ] [ 1 ] 6 [ 1 ] [ 2 ] 7 [ 1 ] [ 3 ] 8 Matrix 2 [ 0 ] [ 0 ] 9 [ 0 ] [ 1 ] 10 [ 0 ] [ 2 ] 11 [ 0 ] [ 3 ] 12 [ 1 ] [ 0 ] 13 [ 1 ] [ 1 ] 14 [ 1 ] [ 2 ] 15 [ 1 ] [ 3 ] 16 Matrix 1 from matrixList [ 0 ] [ 0 ] 1 [ 0 ] [ 1 ] 2 [ 0 ] [ 2 ] 3 [ 0 ] [ 3 ] 4 [ 1 ] [ 0 ] 5 [ 1 ] [ 1 ] 6 [ 1 ] [ 2 ] 7 [ 1 ] [ 3 ] 8 Matrix 2 from matrixList [ 0 ] [ 0 ] 9 [ 0 ] [ 1 ] 10 [ 0 ] [ 2 ] 11 [ 0 ] [ 3 ] 12 [ 1 ] [ 0 ] 13 [ 1 ] [ 1 ] 14 [ 1 ] [ 2 ] 15 [ 1 ] [ 3 ] 16

Помогите пожалуйста с вектором, не имеющим ограничений по количеству элементов. Создаю и добавляю элементы, пока не ругается компилятор.
Выделили память в куче. Обращаться к элементам нужно так.